tl;dr
- Challenge is a VM implemented over signals and ptrace
- Reverse Instruction types and implementation
- Use gdb scripting to find the executed code and get the pseudo VM code
- Find out the algorithm (Max triangle sum) from VM instructions
- Find an more optimized way to solve the problem (Or lazy solve it!).
Challenge Points: 769
Challenge Solves: 7
Solved by: R3x
Initial Analysis
Initial analysis shows us that there are minor changes between this binary and the signal_vm binary - in the way the VM works. Please refer to the writeup of signal_vm for learning about the VM structure.
VM structure
In the first stage of the challenge - we had access to all of the VM registers since they were all in the parent itself. Now in signal_vm_de1ta they are all in the memory space of the child - This makes it hard for us to track what is happening in the VM since we aren’t able to directly view its memory or registers.
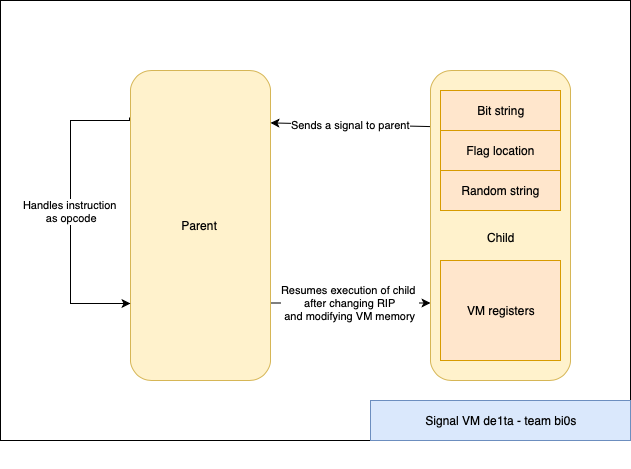
The VM uses the same four signals (SIGTRAP, SIGILL, SIGSEGV and SIGFPE) to serve as instruction classes. However there are a few significant differences from the first stage.
The VM(parent) uses PTRACE_PEEKDATA and PTRACE_POKEDATA to read and write data into the child memory which contains the memory and the registers.
Retrieving VM instructions
We tweaked the script for the old challenge to work for this one. Since we don’t have the register and memory states this time as that happens in the child, we decided to go ahead and write our own code to parse the instructions. So we were able to predict the contents of the VM registers accurately which helped us in figuring out what the child did.
1 | import gdb |
Reversing the VM instructions
This was probably the most complicated VM algorithm I have seen in CTFs. I have written the python version of the code below - you can take a look at it.
1 |
|
Looking a bit deeper into the algorithm we see that it is actually taking the numbers in a very specific order.
| x | z = ((x * (x + 1)) >> 1) | range of y + z |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1..2 |
| 2 | 3 | 3..5 |
| 3 | 6 | 6..9 |
| 4 | 10 | 10..14 |
| … | … | … |
| 100 | 5050 | 5050..5150 |
From this order we figured out that this was basically dividing the array in form of a triangle and then trying to find the path which has the maximum sum.
Now we know what the VM is trying to do and it is taking a long time since the VM is trying to bruteforce the path. Now all we need to do is to find a more efficient way to solve this.
lazy solve
Since it is copying the path that has the maximum sum. I printed out the entire array in the form of a triangle and then I searched for the flag format manually - that is de1ctf{ and then I followed it until I reached the end.

You can probably trace - ~triangle~is from the above screen shot. That was like a wrapper around the flag.
flag was
de1ctf{no~n33d~70-c4lcul473~3v3ry~p47h}
Intended Solution
After talking to the admin at the end of the CTF I learned that this was a DP problem and the solution was pretty simple.
You can take a look at the problem statement and the solution techniques here.