tl;dr
- Open a raw socket.
- Craft the outgoing packets with the byte order of S-PORT, D-PORT, SEQ, ACK reversed.
- Establish the three way handshake in this fashion.
- Send “GET_FLAG” to the server.
Challenge Points: 277
Challenge Solves: 13
Solved by: f4lc0n
f4lc0n solved this challenge after the CTF ended.
Challenge Description
Seems like this server doesn’t respect network byte order.
It swaps byte order in some tcp header fields (sport, dport, ack, seq). Could you get the flag from it?
209.250.241.50:51966
Initial Analysis
On trying to connect to the given service we receive the RST flags in incoming packets indicating the connection being reset.
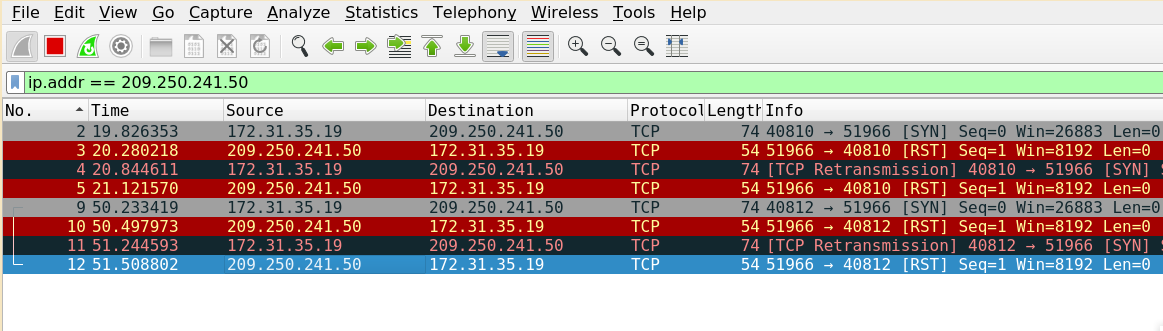
So, as told in the description we need to connect to the server by reversing the byte order of the sport, dport, ack, seq fields.
Now let’s look into the ports section,
1 | import struct |
Given port is 51966. So reversing the byte-order for this number gives 65226
So, we need to send the packets to the port 65226.
Crafting The Packets
IP Headers for all the packets
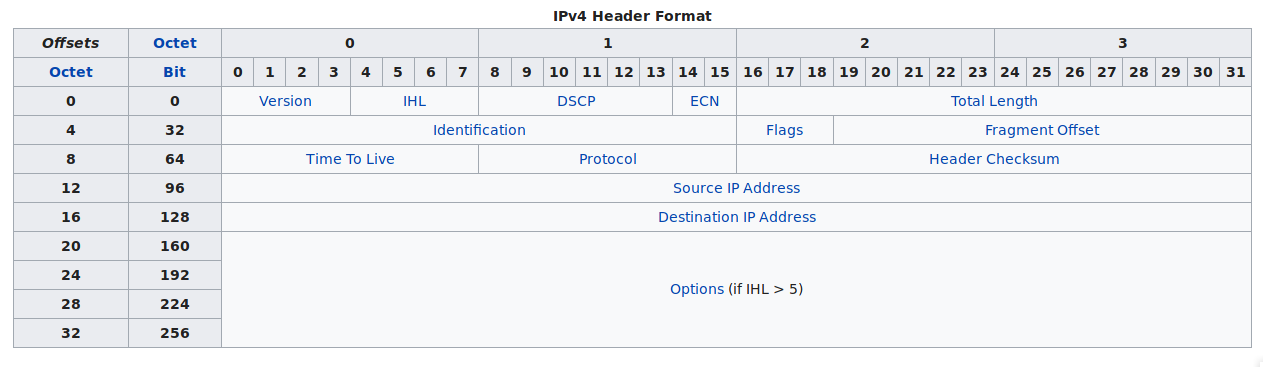
Now let’s craft the IP Headers for the packets
1 | ip-header = '\x45\x00\x00\x28' # Version, IHL, Type of Service | Total Length |
Now we have our ip-header for all the packets ready and let’s craft the packets for the TCP three-way handshake.
TCP Headers for the SYN packet
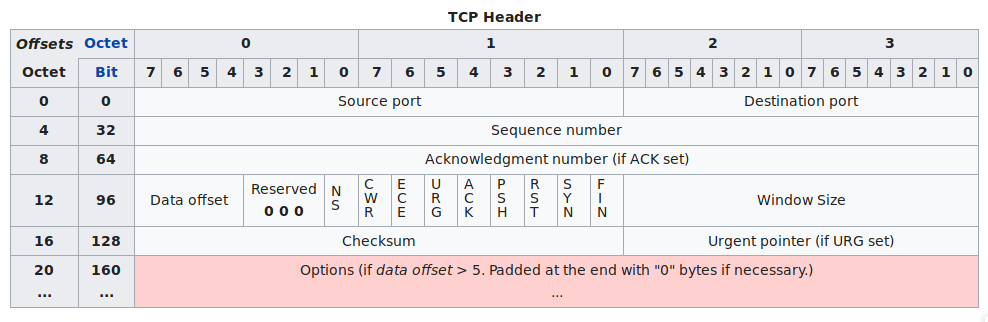
So for the SYN packet we can take the SEQ number anything, for instance let’s take ‘0’
Crafting the SYN packet
1 | tcp-header = '\x39\x30\xfe\xca' # Source Port | Destination Port |
Now let’s send the syn packet to the server and check the response,
1 | import socket |
Let’s look at this process in wireshark,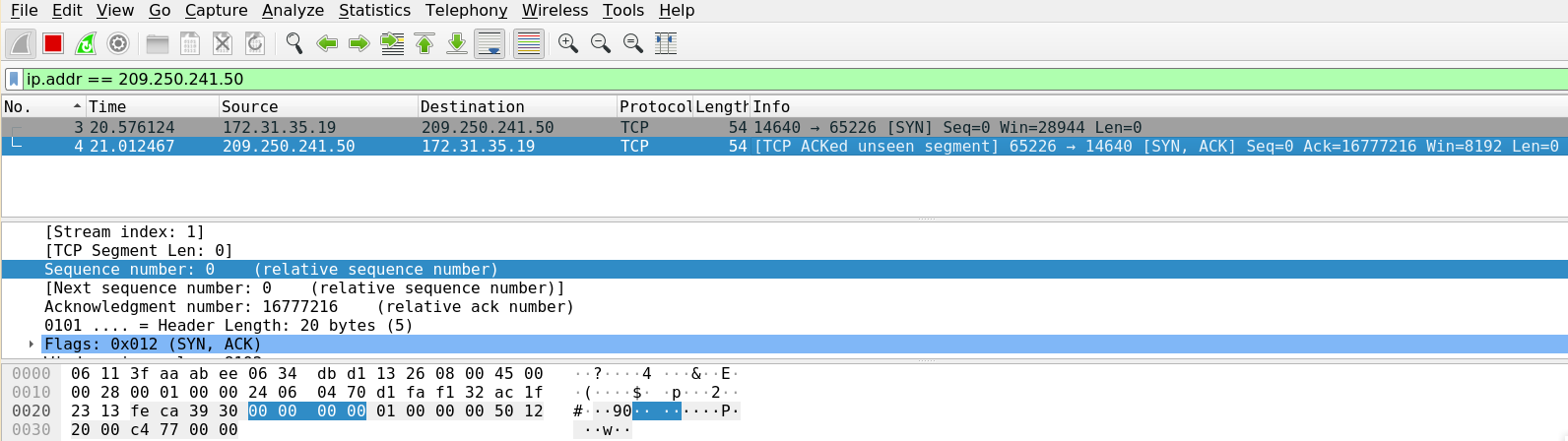
Yayy!! now we’ve received the ACK packet back with the details of the next packets SEQ & ACK numbers.
Crafting the ACK packet
Now let’s craft the tcp header for ACK packet
The SEQ and ACK numbers are based on the SYN-ACK packet from the server.
1 | ack-header = '\x39\x30\xfe\xca' # Source Port | Destination Port |
The SEQ and ACK numbers in this packet are dependent on the [SYN, ACK] packet from the server.
Now lets send the ACK packet and check the response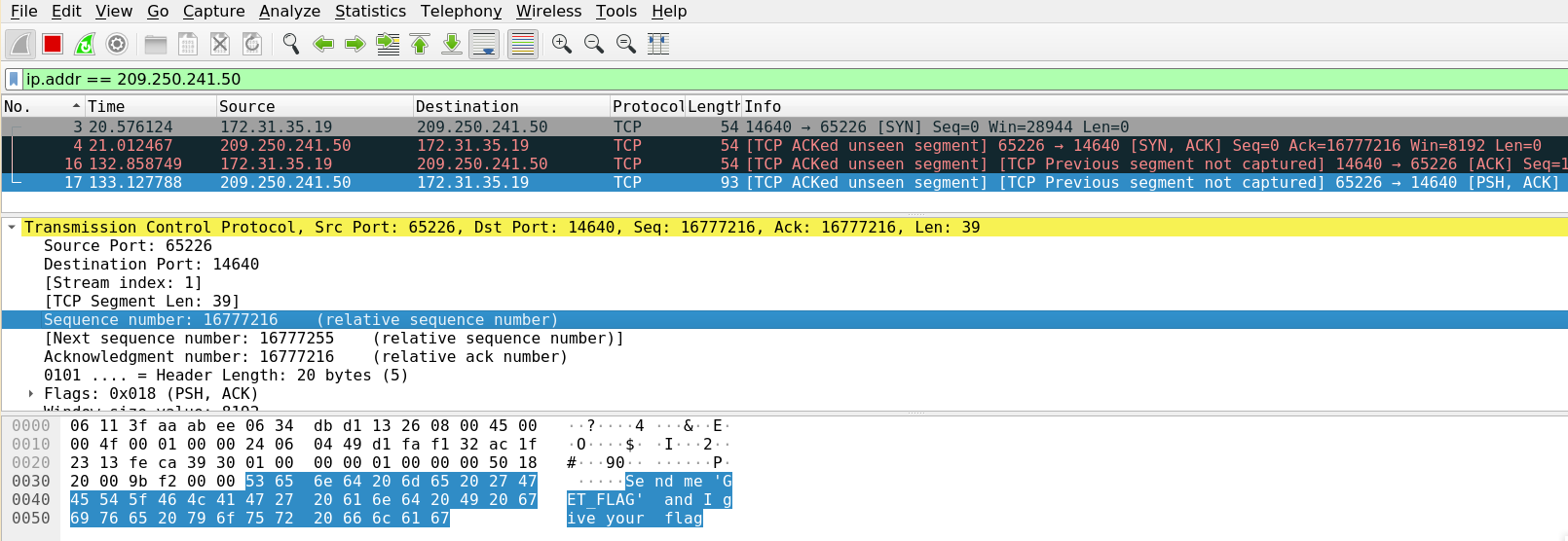
We’ve received a response saying “Send me ‘GET_FLAG’ and I give your flag”
Crafting the PSH-ACK packet
In the last [PSH, ACK] form the server, the length of the data is 39. So we need to add byte-reversed 39 to the last packets SEQ number. Now this number is the ACK number for the next [PSH, ACK] packet to the server.
1 | tcp-header = '\x39\x30\xfe\xca' # Source Port | Destination Port |
After sending this packet we will get the flag in the incoming [PSH, ACK] packet.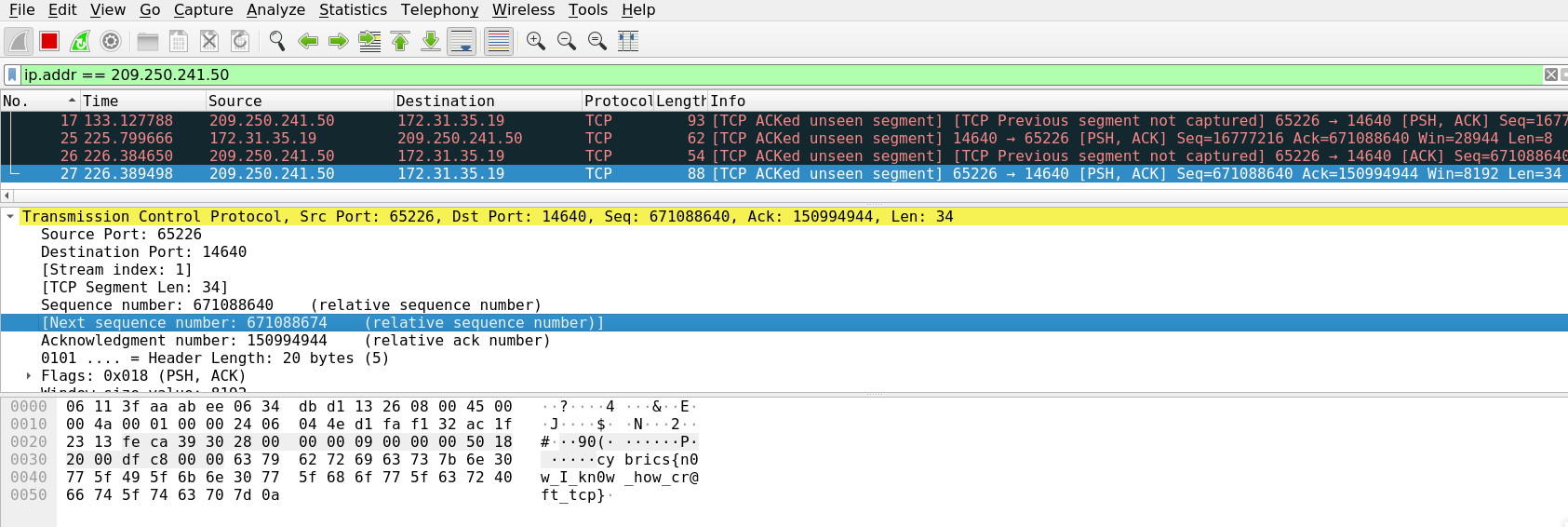
Summing Up
Here’s the final exploit script,
1 | import time |
Run this script and we’ll get the flag in the incoming [PSH, ACK] packet.
Flag: cybrics{n0w_I_kn0w_how_cr@ft_tcp}